With the development of economy and the improvement of people’s living standards, the packaging of goods has become more and more important, and filling machines have also developed greatly. Filling machines are mainly a small category of packaging machines. From the perspective of material packaging, they can be divided into liquid filling machines, paste filling machines, powder filling machines, and granule filling machines. Due to the particularity of liquids (such as solubility, absorbency, convenience of production and transportation, etc.), the production of packaging machines for filling liquids accounts for a large proportion of packaging machinery.
The world’s filling machines are developing towards high speed, versatility and high precision. At present, some filling production lines can be used in different requirements and environments such as glass bottles and plastic containers (polyester bottles), carbonated beverages and non-carbonated beverages, hot filling and cold filling.
At present, the filling speed of carbonated beverage filling machines has reached up to 2000 cans/min. The filling valves of German H&K filling machines are as many as 165 heads, SEN 144 heads, and Krones 178 heads. The diameter of the filling machine is as large as 5 meters, and the filling accuracy is less than ±0.5ml. Non-carbonated beverage filling machines have 50-100 filling valves, the filling speed is up to 1500 cans/min, and the filling machine trough speed is 20-25 rpm, which is 1 times faster. It can be used for hot filling of tea drinks, coffee drinks, soy milk and fruit juice drinks. Foreign hot-filled beverages are no longer sterilized after sealing. Carbonated beverages have been brewing for more than 20 years. Carbonation at room temperature can reduce beverage costs and is beneficial to the environment. The non-carbonated beverage nitrogen filling system uses pressurized or liquid nitrogen dripping methods to infuse liquid nitrogen inert gas into the wall-dropping aluminum cans or PET bottles, so that the two-piece aluminum cans and PET bottles can be used for non-carbonated beverages such as juice drinks, while protecting the contents and reducing the loss of nutrients. At present, PET bottled tea drinks usually adopt hot filling methods. In order to reduce the filling temperature, improve the flavor of tea drinks, and ensure the hygiene and safety of products, PET resin molding has been developed to use 130℃ steam sterilization and special filling aseptic packaging machines. At the same time, aseptic packaging technology for two-piece thin-walled cans of low-acid beverages such as iced coffee is being developed to achieve aseptic packaging of thin-walled cans.
Selection of filling method and quantitative method
Filling method
Due to the differences in the physical and chemical properties of liquid materials, there are different filling requirements during filling. The following methods are commonly used to fill liquid materials from liquid storage devices into packaging containers.
(1) Normal pressure filling
Normal pressure filling is to directly rely on the deadweight of the liquid to flow into the packaging container under atmospheric pressure. The process of normal pressure filling is:
1) Liquid inlet and exhaust: Liquid enters the container, and the air in the container is exhausted at the same time.
2) Stop liquid inlet: When the liquid in the container reaches the quantitative requirement, the liquid inlet stops.
3) Exhaust residual liquid: Exhaust the residual liquid in the air pipe. This process is necessary for those structures that exhaust air to the upper air chamber of the liquid storage tank. Normal pressure filling is mainly used for filling low-viscosity gas-free liquids.
(2) Isobaric filling
Isobaric filling uses compressed air in the upper air chamber of the liquid storage tank to inflate the packaging container so that the pressure is close to equal, and then the filled liquid flows into the container by its own weight.
The process of isobaric filling is as follows:
1) equal pressure
2) liquid inlet and gas return
3) stop liquid inlet
4) release pressure.
Isobaric filling is suitable for filling carbonated beverages such as beer, soda, etc., to reduce the loss of contained gas.
(3) Vacuum filling
Vacuum filling is filling under conditions below atmospheric pressure. There are two basic methods: one is differential pressure vacuum, which keeps the liquid storage tank at normal pressure and only evacuates the inside of the packaging container to form a certain vacuum degree. The liquid flows into the packaging container by the pressure difference between the two containers. The other is gravity vacuum, which keeps the liquid storage tank and the packaging container in a nearly equal vacuum state. The liquid flows into the container by its own weight. At present, differential pressure vacuum is commonly used in China. It has a simple structure and reliable operation.
The process of vacuum filling is as follows:
1) vacuuming the bottle
2) liquid inlet and gas return
3) stop liquid inlet
4) residual liquid return.
Vacuum filling is suitable for filling liquids with high viscosity and toxic liquids. This method can not only increase the filling speed, but also reduce the contact and interaction between the liquid and the residual air in the container, so it is beneficial to preserve the product. It can also limit the dispersion of toxic gases and liquids, thereby improving the operating conditions. However, it is not suitable for filling alcoholic beverages containing aromatic gases.
(4) Siphon filling
Siphon filling is to use the siphon principle to suck the liquid into the container through the siphon tube until the liquid levels of the two are equal. Siphon filling is suitable for filling low-viscosity liquids without gas. It has a simple structure, but the filling speed is low.
(5) Pressure filling
Pressure filling is to use mechanical or gas-hydraulic devices to make the piston reciprocate to suck the liquid with high viscosity from the liquid storage tank into the piston cylinder, and then force it into the container to be filled. This method is sometimes also used for filling beverages such as soda, and can be directly poured into the bottle by relying on its own air force. When choosing a filling method, in addition to considering the viscosity characteristics of the liquid itself, it is also necessary to carefully analyze the process requirements of the product and the structure and operation of the filling machinery and equipment. At the same time, during the filling process, it is also required to reduce the contact between liquid and air and try to eliminate the influence of residual air in the bottleneck.
Quantitative methods
Liquid quantitative measurement mostly uses volumetric quantitative method, which can be roughly divided into the following three types.
(1) Liquid level control quantitative method The liquid level control quantitative method is to achieve the quantitative value by controlling the liquid level of the container being filled during filling.
(2) Quantitative cup quantitative method The quantitative cup quantitative method is to first inject the liquid into the quantitative cup and then fill it. If liquid loss is not considered, the liquid volume filled each time should be equal to the corresponding volume of the quantitative cup.
(3) Quantitative pump quantitative method The quantitative pump quantitative method is a quantitative method that uses mechanical pressure filling. The volume of the material filled each time is proportional to the reciprocating stroke of the piston.
Comparing the above three quantitative methods, it is not difficult to understand that the second method is directly affected by the volume accuracy of the bottle and the sealing degree of the bottle mouth, so its quantitative accuracy is poor, but the structure is simple and it is still used today. In fact, when choosing a quantitative method, the first thing to consider is the accuracy required by the product. The quantitative accuracy is related to the product. The more expensive the product, the smaller the measurement error should be. In addition, the process characteristics of the liquid itself should also be considered when choosing a quantitative method.
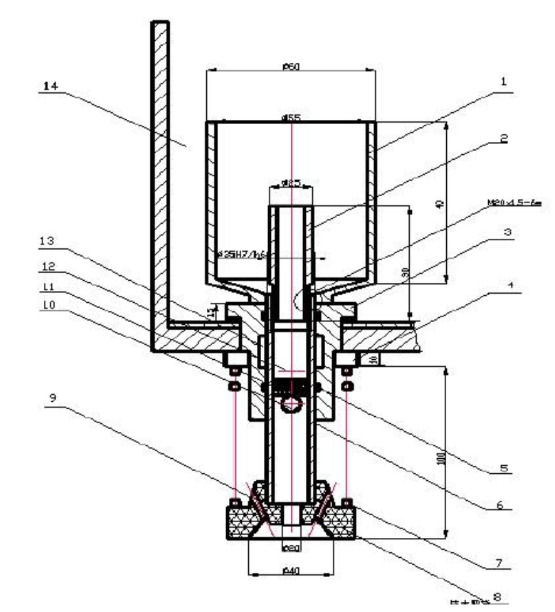
Customized Filling Machine
1. Determine the function and application scope
Most of the early filling machines had a single function, which could simplify the design and make them easier to succeed. If multiple machines and multiple processes are combined into one package, significant economic benefits can be achieved.
When determining the functions and application scope of a filling machine, two issues need to be considered:
(1) Reliability. In general, as the functions increase, the filling operation links increase, and the possibility of failure also increases accordingly. Therefore, only when the operations of single-function filling are quite stable and reliable can we consider combining them into a multifunctional filling machine.
(2) Adaptability. The application scope of any filling machine is limited. The more functions the machine has, the more complex the structure. Therefore, multifunctional filling machines are often designed in a combined form, and some combined components can be flexibly added or modified according to the different needs of users.

2. Process analysis
Process analysis is to study, analyze and determine the process methods for the designed packaging machinery to complete the expected packaging process. Several issues need to be considered:
Packaging method
(1) Give priority to ensuring filling quality. Regardless of the filling method used, filling quality must be guaranteed. (2) When there are multiple methods to choose from, the one that is easy to implement should be selected.
Machine type
(1) Select the machine type based on the number of filling actuators. (2) Select the machine type based on the productivity.
Packaging procedures, packaging technology and number of workstations
(1) Packaging procedures refer to the order in which packaging operations are completed. The packaging method often determines the packaging procedures.
(2) Packaging process route: includes the supply route of packaging materials and packaging items, as well as their transmission route during the packaging process and the output line of the packaged products.
Motion requirements and mechanism selection Analyze and determine the motion requirements for the actuator based on the given functions, application conditions and scope, and process methods, and then complete the mechanism selection and its integration.
3. Overall layout
The overall layout refers to the reasonable configuration of the relative spatial positions of the relevant components of the filling machine.
(1) Arrangement of actuators
(2) Layout of the transmission system
(3) Arrangement of operating conditions
(4) Selection of support form
(5) Drawing of the overall layout
4. Formulate the main working parameters
The main technical parameters of filling machinery:
- Institutional parameters
- Motion Parameters
- Power parameters
- Process parameters
5. Proposal
For example:Application: Packaging low-viscosity, non-gased liquid beverages (such as mineral water, beverages, etc.).
Packaging specifications: Filling mineral water/beverages.
Filling bottle specifications: filling volume 600ml, diameter 60mm. Packaging material: plastic bottle/glass bottle.
Filling capacity: >100,000 bottles/day. Filling time: <12s/time
Design requirements: simple structure, low cost, good working stability, easy to control.
Main technical indicators of filling machinery: (1) Filling liquid viscosity is less than 1Pa.s (2) Filling speed 6 times/min (3) Filling container size range: height 20mm—200mm, cross-sectional diameter <70mm (4) System pressure: 0.5—3Mpa
You can choose your requirements and we will provide you with the most suitable canning machine. Don’t hesitate to contact customer service now.









